- Oak Brook:(630) 705-9999
- Chicago:(312) 920-8822
- Email:inquiry@vervecollege.edu
- Make a Payment
- Home
- Programs
- Admission
- Resources
- ATI Entrance Exam Resources
- New E-Digital Library
- Refer a Friend
- School Newsletter
- Events
- Employers
- Job-Network
- Alpha Beta Kappa Candidates
- Verve College Library
- Graduation and Pinning Ceremony Photo Galleries
- Textbook Information
- Career Services
- Tutoring
- School Catalog
- FAQ
- Constitution Day Program
- Alumni
- Verve College Plans
- Financial Aid
- HEERF Reporting
- Satisfactory Academic Progress
- Apply For Financial Aid
- Net Price Calculator
- Return of Title IV Funds (R2T4)
- Financial Aid Office Code of Conduct
- Contact
- FAQs
- Verification Policy
- Vaccination Policy
- Student Right-to-Know Act
- Misrepresentation
- Information Security Program
- Academic Award Year
- Availability of Employee
- Cost of Attendance
- Health & Safety Exemption Requirement
- Students Rights and Responsibilities
- Leave of Absence
- Pell Formula
- Military Students
- Grants/ Scholarship Policy
- Contact Us
- Testimonials
- Blog
Is a Nursing Career Right For You?
Take The Free Quiz
How to Study Cadavers, Models, and Diagrams Effectively?
How to Study Cadavers, Models, and Diagrams Effectively?
Learning human anatomy is a core requirement for anyone pursuing a career in healthcare. For students enrolled in an A&P prep course, Illinois institutions offer, anatomy can initially feel overwhelming due to the volume of information and the need to understand the human body in three dimensions. Cadavers, anatomical models, and diagrams are the primary tools used to teach anatomy, but many students struggle because they do not know how to use these resources effectively. Studying anatomy is not about memorizing labels; it is about developing spatial understanding, clinical relevance, and long-term retention.
This blog explains practical and effective ways to study cadavers, models, and diagrams so students can learn anatomy with confidence and clarity.
Key Takeaways
- Cadavers help students understand real human anatomy, including natural variations and spatial relationships.
- Anatomical models simplify complex structures and improve clarity during revision.
- Diagrams strengthen conceptual understanding and support long-term memory.
- Combining all three learning tools leads to deeper comprehension and better academic performance.
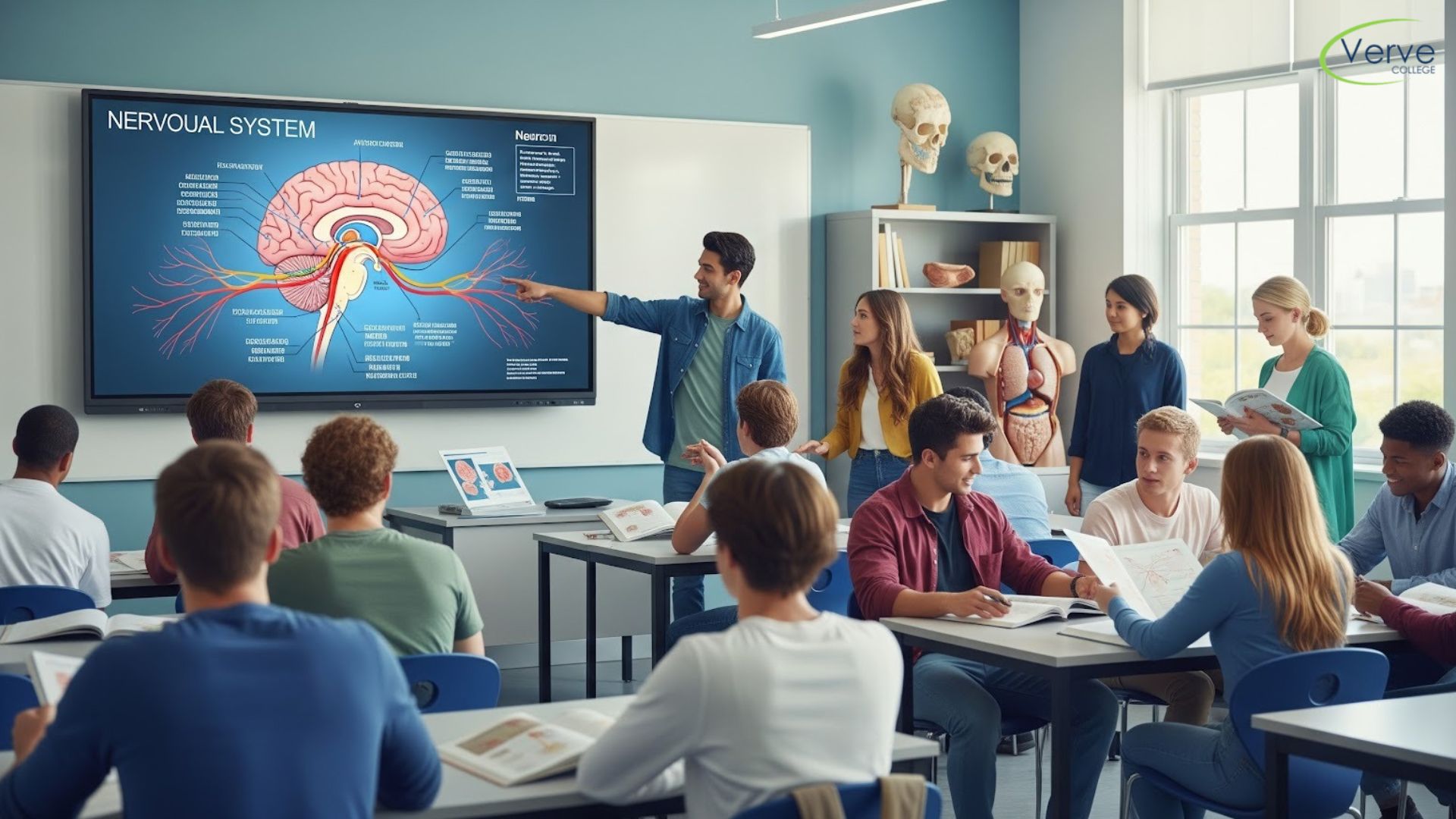
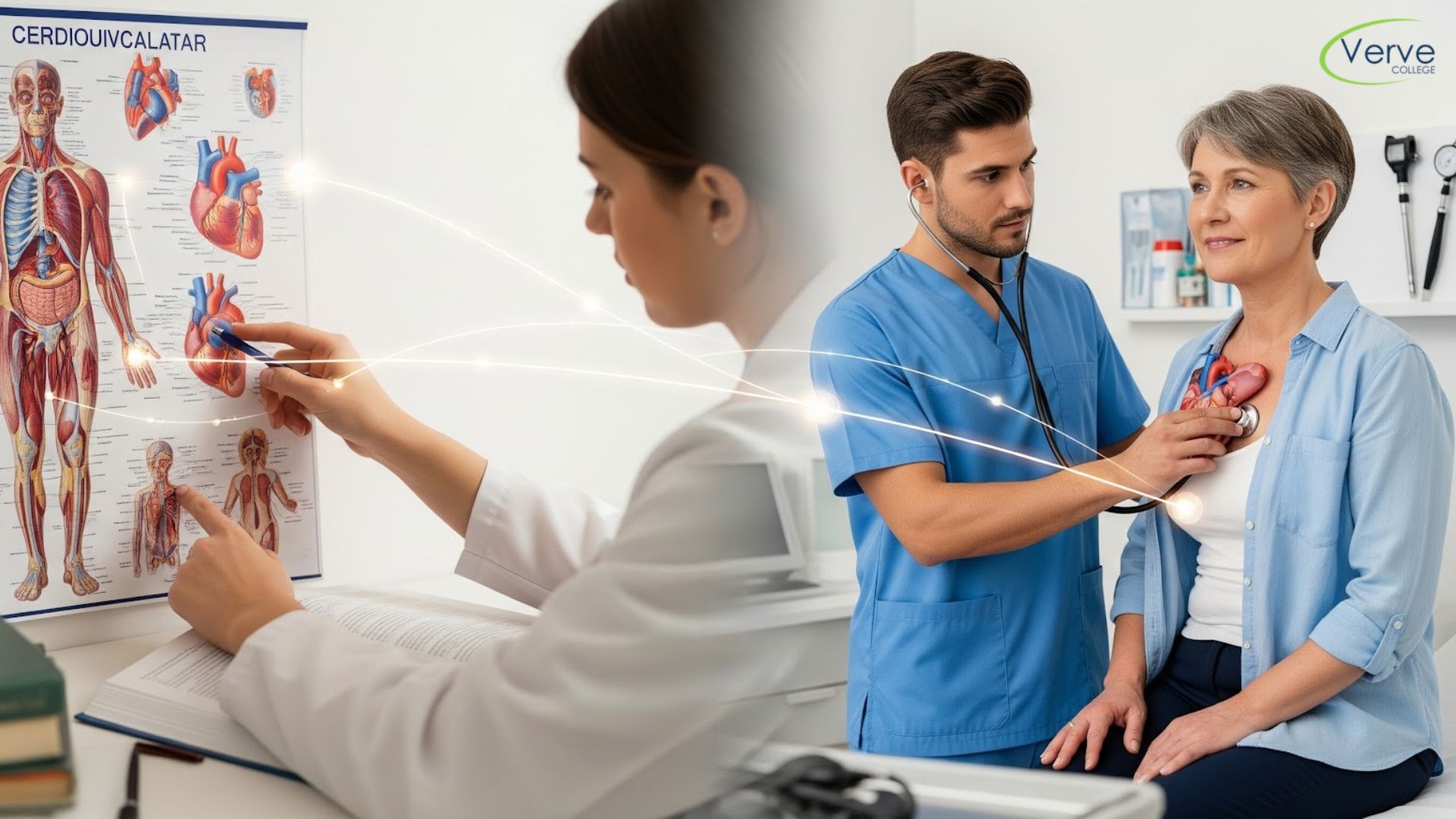
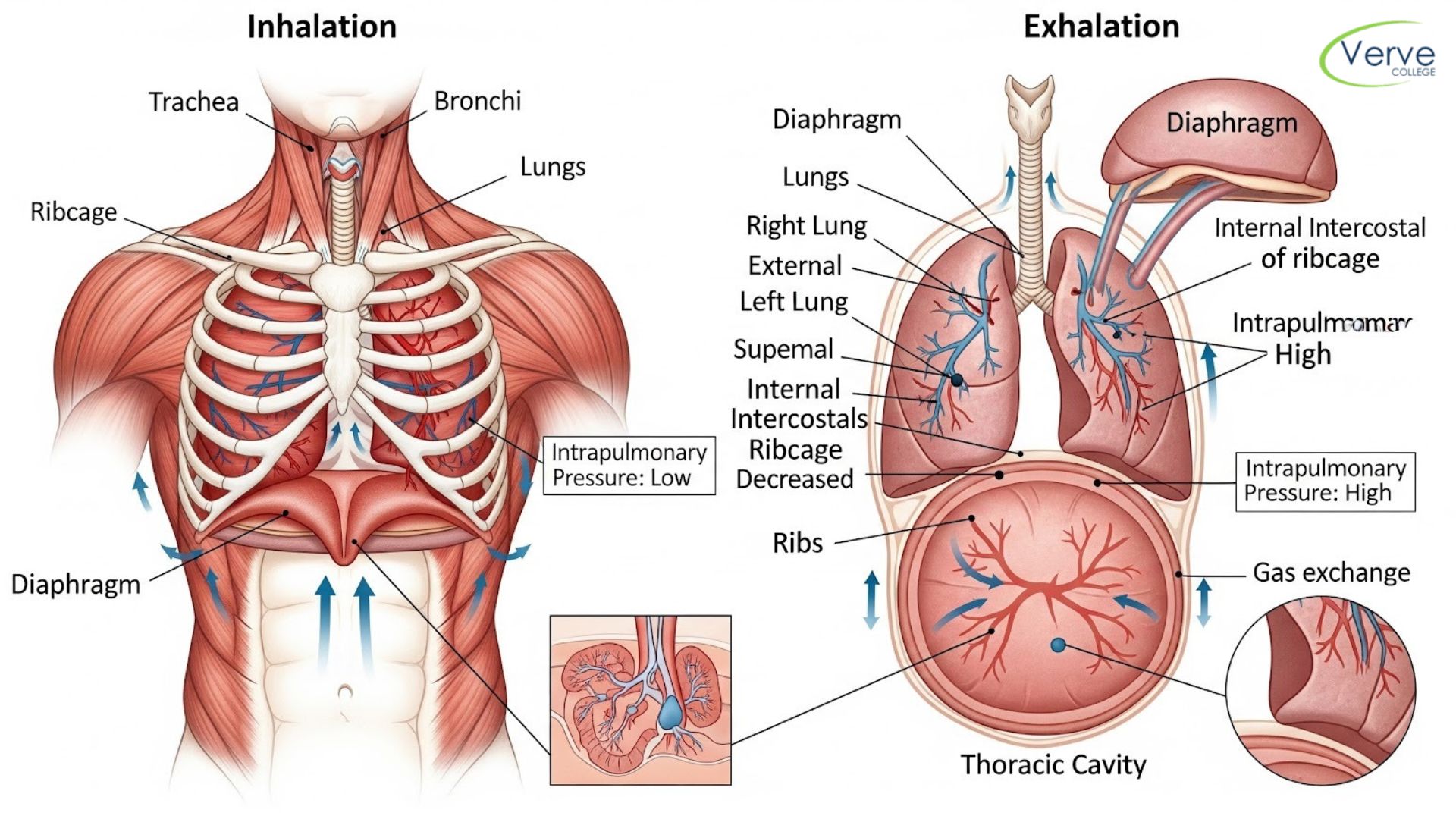
Understanding the Role of Cadavers in Anatomy Learning
Cadaver-based learning provides students with a realistic view of the human body that no textbook can fully replicate. Studying cadavers allows learners to understand how organs, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels exist in relation to one another. To use cadavers effectively, students should always prepare before entering the lab by reviewing anatomical structures in advance. This preparation reduces confusion and helps students identify structures more confidently during dissection sessions.
While observing cadavers, it is important to move beyond identification. Students should focus on understanding function, orientation, and clinical significance. For example, noting how nerves travel alongside blood vessels or how muscle attachments influence movement builds applied knowledge. Repeated exposure to cadaver labs further enhances spatial awareness and reinforces learning, making anatomy more intuitive over time.
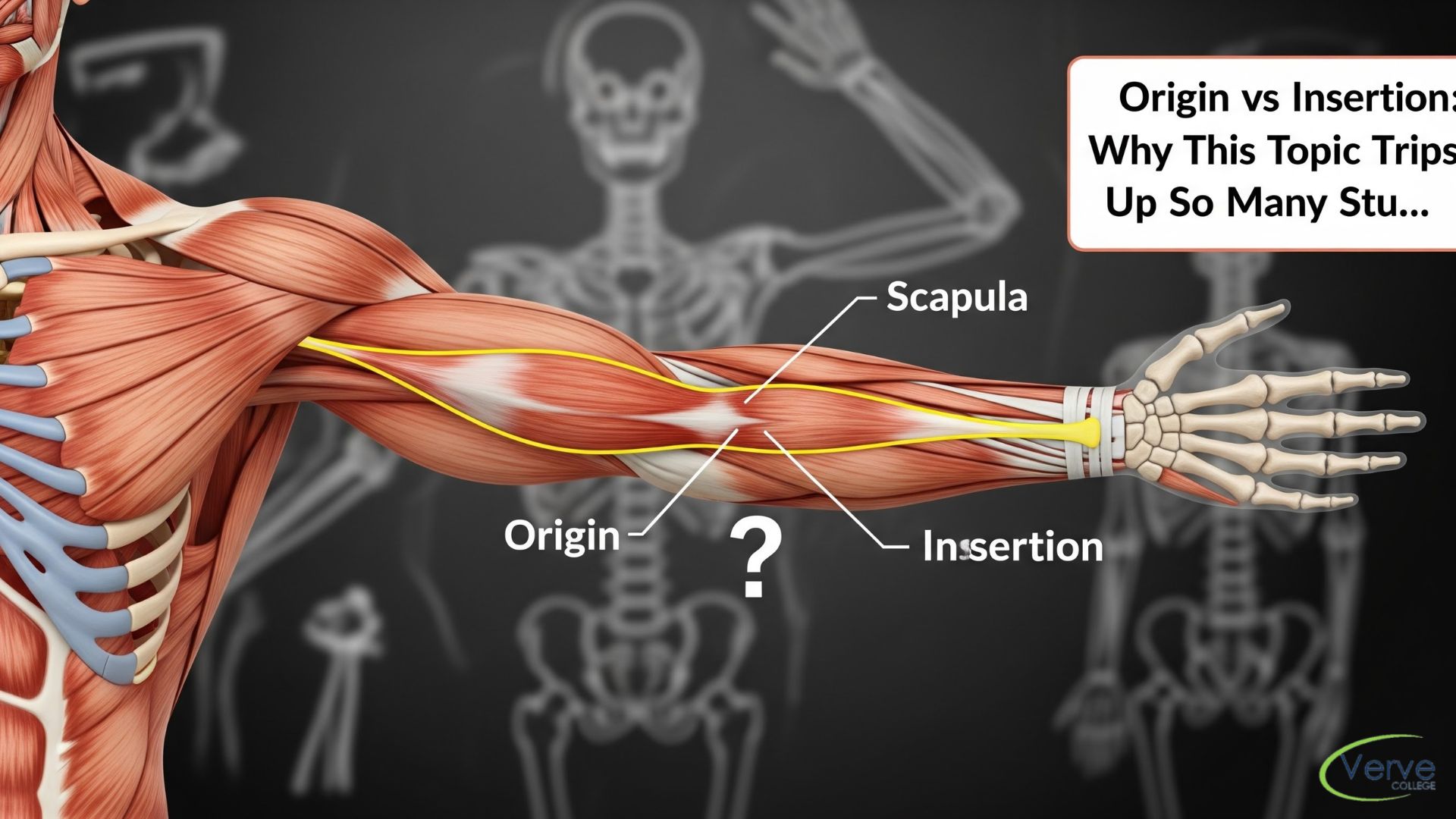
Using Anatomical Models for Structured Learning
Anatomical models serve as an excellent bridge between theory and real anatomy. These models present clean, well-defined representations of structures, which is especially helpful when certain details are difficult to visualize in cadavers. Models allow students to isolate specific systems, such as the skeletal or muscular system, and understand them without distraction.
For students enrolled in demanding programs such as evening LPN programs, models are particularly useful because they support efficient studying within limited time frames. By handling and examining models closely, learners can better grasp structural relationships and revise key concepts quickly. Using models alongside textbooks and lab experiences strengthens understanding and improves recall during exams.
Learning Effectively with Diagrams and Visual Resources
Diagrams play a vital role in anatomy education by simplifying complex information into clear visual formats. They help students understand orientation, layers, and pathways that may not be immediately obvious in physical specimens. Studying diagrams before lab sessions prepares students to recognize structures, while reviewing them afterward reinforces what was observed.
One of the most effective ways to use diagrams is active recall. Redrawing diagrams from memory and labeling structures helps identify gaps in understanding. Consistent use of diagrams builds strong mental maps, making it easier to recall anatomical details during assessments and clinical discussions. Over time, diagrams become powerful tools for both learning and revision.
Integrating Cadavers, Models, and Diagrams
The most successful anatomy students do not rely on a single study method. Instead, they integrate cadavers, models, and diagrams into a structured learning process. Studying diagrams before lab sessions creates familiarity, observing cadavers provides real-life context, and reviewing models afterward reinforces clarity.
This integrated approach is especially important for students attending nursing schools in Chicago, IL, where academic expectations are high and clinical readiness is essential. When students connect visual learning with hands-on experience, anatomy becomes easier to understand and retain. Using these tools together ensures balanced learning and reduces the likelihood of rote memorization.
Building Consistency and Confidence in Anatomy Study
Consistency is key when studying anatomy. Regular review sessions, even short ones, help prevent information overload and improve long-term retention. Students should revisit previously learned systems while progressing to new ones to maintain continuity. Discussing anatomy with peers or explaining concepts aloud also strengthens understanding.
Confidence develops when students feel familiar with anatomical structures across different learning formats. As learners repeatedly encounter the same structures in cadavers, models, and diagrams, recognition becomes faster and more natural. This confidence not only supports academic success but also prepares students for clinical environments where anatomical knowledge is applied daily.
Conclusion
Studying cadavers, models, and diagrams effectively requires strategy, preparation, and integration. Each learning tool offers unique benefits, and together they provide a comprehensive understanding of human anatomy. When students engage actively with these resources, anatomy becomes less intimidating and more meaningful.
By developing strong study habits early, learners can build a solid anatomical foundation that supports both academic achievement and professional growth. Effective anatomy learning is not about memorizing more but about understanding better.
FAQs
How should beginners approach cadaver study for the first time?
Beginners should review diagrams and textbooks before entering the lab to gain familiarity. This preparation helps them identify structures confidently and reduces anxiety during dissections.
Are anatomical models enough for exam preparation?
Models are excellent for clarity and revision, but they work best when combined with diagrams and cadaver exposure. Using multiple resources ensures a deeper understanding and better recall.
What is the best way to remember anatomy long-term?
Long-term retention improves through repetition, active recall, and integration of learning tools. Regular review and practical application help reinforce anatomical knowledge over time.
 Sign up
Sign up Login
Login